Our Contribution
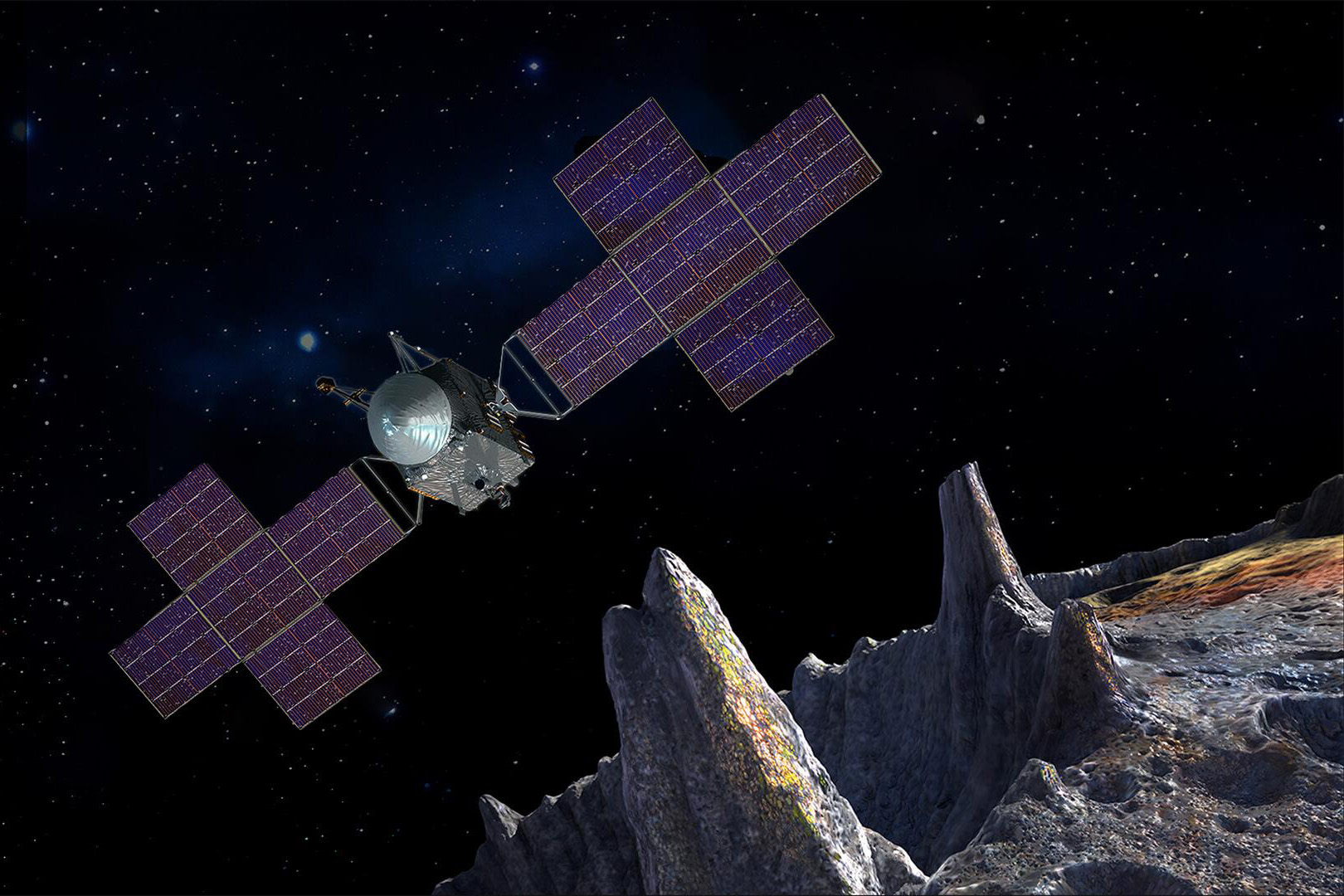
Exploring a Metal Asteroid
The Psyche Gamma-Ray and Neutron Spectrometer (GRNS) will investigate the composition of a unique, metal-rich asteroid to provide clues about the formation of rocky planets.
The Psyche Gamma-Ray and Neutron Spectrometer (GRNS) will investigate the composition of a unique, metal-rich asteroid to provide clues about the formation of rocky planets.
Instrument Type
Gamma-Ray and Neutron
The NASA Psyche mission will explore Psyche, a unique, metal-rich asteroid in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter that may be an exposed nickel-iron core of an early planet. The goal of the mission is to characterize Psyche’s composition and geology to better understand how planetary bodies have formed and changed over time. APL will provide the Psyche GRNS, which will quantify Psyche’s elemental composition.
The GRNS consists of a gamma-ray spectrometer (GRS) and a neutron spectrometer (NS). The GRS uses a high-purity germanium sensor designed and built in partnership with Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, and is the state-of-the-art technology for achieving high-sensitivity gamma-ray spectral measurements. The NS uses three helium-3 gas proportional sensors to measure neutrons in three broad energy ranges. The Psyche GRNS builds on a similar APL-developed GRNS flown on the successful MESSENGER mission that explored the planet Mercury.
Planetary gamma-ray and neutron spectroscopy is a widely used technique to remotely measure the elemental composition of planetary bodies. APL has significant experience in carrying out such measurements for the NASA MESSENGER and NEAR missions. Additional APL-led gamma-ray and neutron spectroscopy measurements are planned for the Japanese Martian Moons eXploration (MMX) mission and NASA’s Dragonfly mission.
Learn more about the different components of the Psyche GRNS below.
All photos: Johns Hopkins APL/Ed Whitman
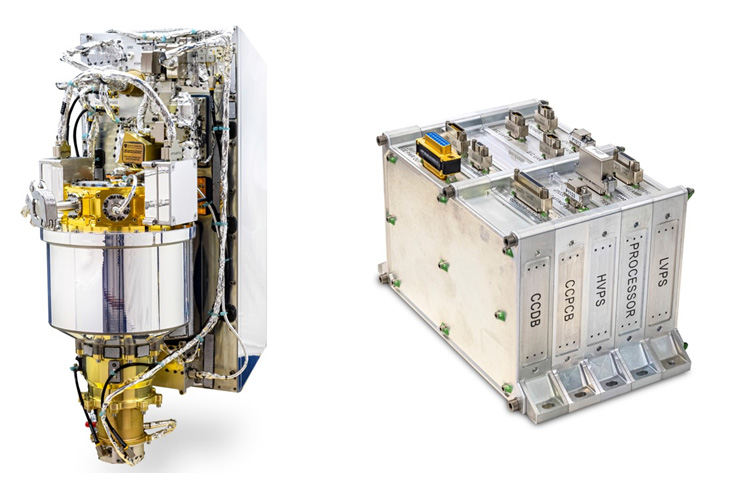
The gamma-ray spectrometer (left) and its data processing unit (right). The GRS will measure gamma rays to characterize and quantify the elemental composition of the metal-rich asteroid Psyche.
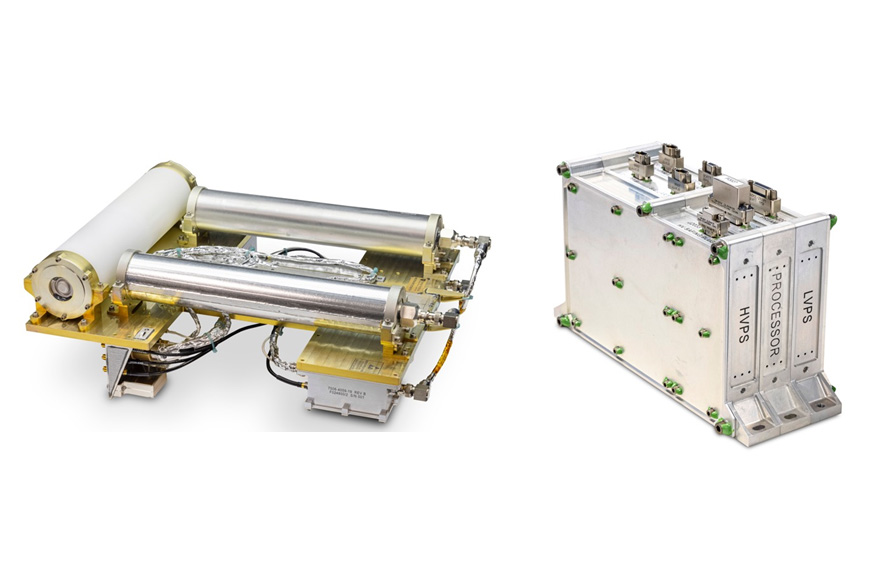
The neutron spectrometer (left) and its data processing unit (right). The NS will measure three energy ranges of neutrons to characterize and quantify the elemental composition of the metal-rich asteroid Psyche.
NASA’s Psyche mission launched on October 13, 2023, and is now heading to map and study a metal-rich asteroid called Psyche. The asteroid sits between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, and it may be the vestigial core of a planet from the beginning of the solar system, providing a rare investigational opportunity that could reveal how Earth’s and other planetary bodies’ cores came to be.

This website uses cookies to measure traffic and improve your experience. View our Privacy Policy to learn more.
